video tutorials for social media
What is the Difference Between Translation and Transcription?
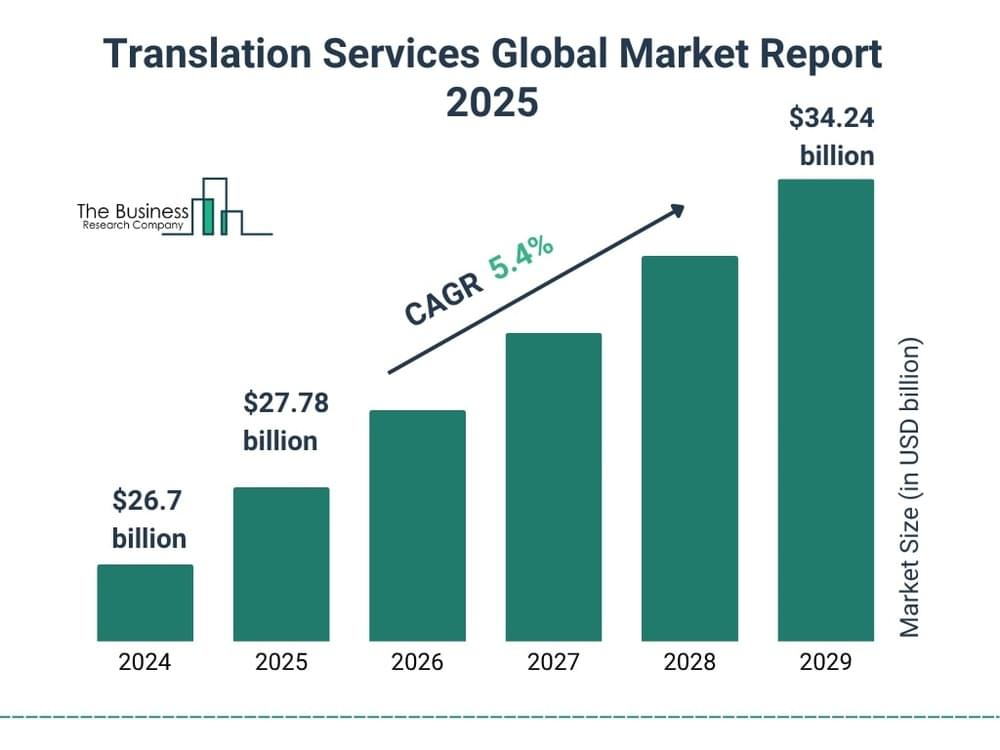
Language and content processing sometimes involve two terms that sound very similar but are two completely different things: transcription and translation. If you are working in any form of content creation or are especially related to business, education, law, or medicine, then understanding the difference between translation and transcription brings clarity and accuracy to your work.
Since around 75% of viewers watch videos on mute, adding subtitles through transcription or translation is no longer optional; it is a must for wider reach.

For someone who deals with subtitling of webinars, tutorials, or podcast videos, transcription and translation are everyday tasks. If you keep reading, we shall discuss what translation and transcription are and what the difference is between the two.
Table of content:
- What are transcription and translation?
- What is the difference between transcription and translation?
- Transcription vs. translation
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What are transcription and translation?
Translation and transcription are used to convert the language of a video or audio content, but they have separate purposes. One turns spoken words into written text in the same language (transcription), while the other carries meaning across languages (translation).
What is transcription?
Transcription is the act of converting spoken language into written text in the same language. Imagine listening to an interview and typing out every word exactly as it was said. That is transcription.
Transcription is converting spoken words into written text in the same language. It is not just about writing down words, it is about capturing conversation or speech carefully to create a WRITTEN RECORD. This process is excellent for many industries that rely on accurate documentation.
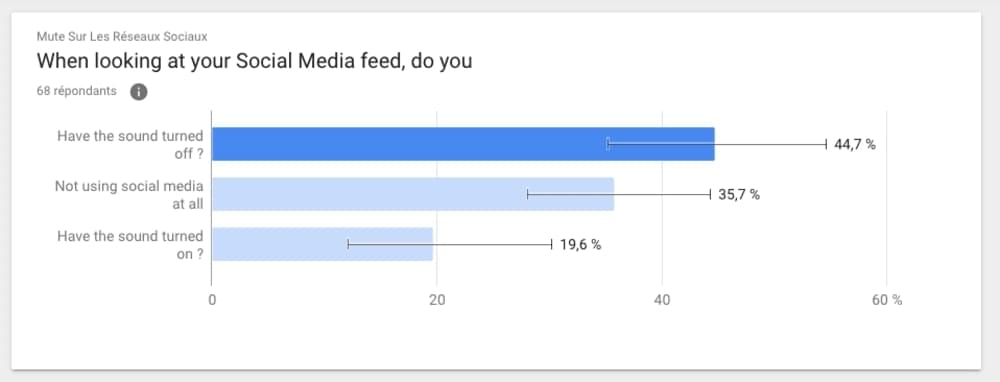
Good transcripts help the accessibility of your content because viewers who are deaf or hard-of-hearing can easily follow along with your content. They also improve video SEO because search engines can list the dialogues, and so your video becomes more discoverable. Plus, viewers in silent environments or noisy offices can still understand the video via captions. Around 85% of the audience views content without sound.
Types of transcription
Transcription comes in a few flavors depending on the level of detail needed:
1. Verbatim transcription is a word-for-word speech-to-text conversion, including every “um,” “uh,” and filler sound. This is useful for people who are hard of hearing, and for research, legal records or media contexts. Example: “Well, um, I think—yeah—I think we should go.”
2. Intelligent (or Summary) transcription: requires the transcriber to clean up speech by removing filler words and to adjust words for clarity without changing meaning. Intelligent transcription is used for meeting minutes, lecture summaries, or reports. For example: a speaker says 5 sentences about why a product is great; transcript reads: “The speaker praised the product’s quality and usability.”
3. Clean (or Edited) transcription focuses on clear, readable text without changing the meaning. It removes fillers, repetition and irrelevant noises. Edited transcription is common for subtitles, articles, or corporate materials. Example: “I think we should go.”
Each style has a different purpose depending on whether you need the raw speech or a polished document.
When to use transcription?
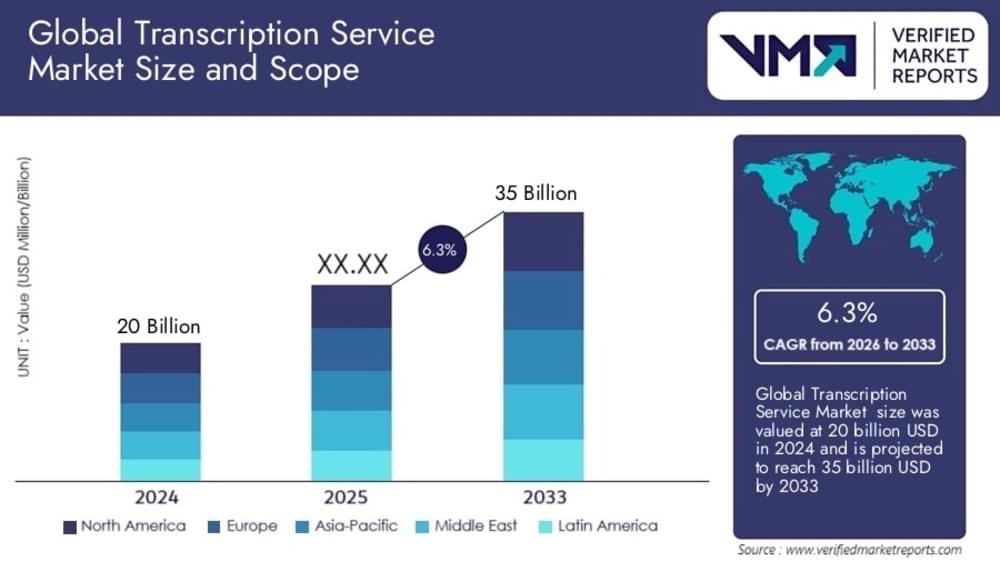
Transcription is used in many areas like law, education, media, and business. In 2024, the transcription service market had a value of $20 Billion and now it is projected to reach $35 billion by 2033.
Here’s how it works in different fields:
- Legal: Court reporters transcribe hearings and depositions, while lawyers use transcripts of client and witness interviews to prepare cases.
- Journalism: Journalists transcribe interviews to ensure every quote in articles, documentaries, and news reports is accurate.
- Media: Creators transcribe videos, podcasts, and films to add subtitles, captions, or turn them into blogs and articles for wider reach.
- Music: In music, transcription means writing performances into musical notation.
- Research & Academia: Researchers transcribe interviews and discussions for analysis. In education, lectures and seminars are transcribed into study materials.
- Business: Companies transcribe meetings, conferences, and customer feedback to keep clear records and improve services.
- Medical: Doctors and surgeons transcribe notes, consultations, and recordings into medical reports for hospitals and institutes.
What is translation?
Translation is when you convert written or spoken words from one language into another. The aim here is to maintain meaning, tone, and cultural relevance between languages. For example you translate your English video into Spanish so Spanish viewers can understand and enjoy it.
Translation requires more than just the words and grammar of two languages. It requires an understanding of the message’s context, purpose, and its cultural nuances for translation accuracy. In the past, businesses worked with skilled human translators who carefully translated the meaning and the emotional tone of the original content.
Today, automated tools give fast results and they save a lot of time, however, they often miss the delicate details of the language and cultural sensitivity that only a human translator can provide. Therefore, human expertise is still necessary for high-quality translations.
Cultural context matters in all types of translations because a direct word swap might be meaningless in another language. Translation is adopting the sense of your content so it feels more natural to the target audience even when your content is not in their native language. Translation helps people to communicate without any language barriers and without losing the original message’s depth 2.
Types of translation
Literary translation is used for books, poems, and scripts that call for attention to tone and style. Technical translation is used for manuals, instructions, and scientific documents requiring precision. Legal translation style is often used for contracts, laws, and official documents where exact wording affects outcomes. Localization style of translation is for adapting content to fit cultural norms, such as marketing materials or software interfaces.
When to use translation?
Translation is done when you already have a written script and don’t need timestamps and when your goal is to localize the content into another language, and timing details are less important.
These are industries that benefit from the translation supports globally the most:
- Legal: Law firms and courts translate contracts, judgments, and immigration files so everyone understands rights and duties. Certified translations are used for visas, company registrations, and cross-border cases.
- Medical & Healthcare: Hospitals and device makers translate consent forms, instructions, and clinical protocols to protect patient safety and avoid errors.
- Business & Corporate: Companies translate HR policies, training, and marketing materials to align teams and connect with customers worldwide.
- Education: Schools and edtech platforms translate syllabi, courseware, and certificates to support students, online learning, and global enrollment.
- Technology & Software: Product teams translate app interfaces, help guides so software can be used in different languages.
- Media & Entertainment: Studios and streaming services translate scripts, subtitles, and dubbing to make films and podcasts accessible to global audiences.
- Government & Public Services: Agencies translate laws, tax forms, and public notices so residents and partners can follow rules and access services.
- Tourism & Hospitality: Hotels, airlines, and attractions translate websites, menus, and safety guides to make travel easy for international visitors.
- Scientific Research: Researchers translate papers, abstracts, and lab protocols to share discoveries.
- Finance & Banking: Banks translate forms, statements, and investor documents for clients speaking different languages.
- Literature & Publishing: Publishers translate novels, children’s books, and comics to reach new readers in different languages.
- Religious Texts: Faith communities translate scriptures, sermons, and study guides to share beliefs.
Translation breaks down language walls and opens doors to views and opportunities otherwise inaccessible.
What is the difference between transcription and translation?
Transcription and translation sound very similar, but only when we look at them side-by-side, their differences become more evident. If you are looking to translate or transcribe and are wondering how transcription and translation are actually different from each other, here’s the simple point-by-point, detail:
- Translation converts spoken or written content from one language to another, whereas transcription writes down spoken content exactly as it is heard, in the same language.
- Translation aims for accuracy of communication between the two languages, whereas transcription aims for accuracy of words.
- Translation may change wording or phrasing according to cultural context, whereas transcription keeps the original wording exactly as it was spoken in your audio or video.
- Translation requires the translator to be fluent in the two languages, but transcription requires strong listening and typing skills in one language.
- Translation can be done from text-to-text or from speech-to-text, whereas transcription is always done for audio or video content.
Transcription vs. translation
To make the difference between transcription and translation easier, here is the comparison in a tabular form:
| Feature | Transcription | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Language | Same as spoken in audio or video | Different from original content |
| Focus | Accuracy | Conveying meaning in new language |
| Skills | Listening and typing | Reading, speaking, listening, editing and writing skills |
| Complexity | Less complex as the content is written as it is | More complex due to contextual and cultural nuances |
| Input | Spoken content | Written and/or spoken content |
| Output | Written content | Written and/or spoken content |
| Use | Captions, scripts, SEO | Multilingual subtitles, international reach of the content |
How to decide what you need? Translation vs transcription
Not sure what you need: transcription vs translation, or both? The questions below will help you decide quickly. Just see which situation matches your need and follow the suggested solution.

| Question | You need |
|---|---|
| Do you need written text from your audio or video in the same language for notes, records, or documentation? | Transcription |
| Do you want your content to be understood by people who speak different languages? | Translation |
| Do you need a written record AND its version in another language to share with international teams or clients? | Both |
| Do you want to make lectures, interviews, or podcasts easier to read and reference in their original language? | Transcription |
| Do you want to adapt your message so it feels natural to local audiences in different regions? | Translation |
| Do you need subtitles or captions that show both the original words and their translations on screen? | Both |
Do you need reliable transcription and translation services? Use SubtitleBee
Do you ever wish your audio or video could reach more people, in many languages? SubtitleBee makes that super easy because it uses smart tools to help you, step by step.
SubtitleBee is an AI-powered platform that can transcribe your audio to text in just minutes. It supports more than 120 languages, so your content can reach a global audience. You can choose regional dialects too like Mexican Spanish or Spain Spanish for even richer results on SubtitleBee.
For Subtitlebee users, the most effective sequence is to transcribe first, then translate. You can buy any price plan and get complimentary transcription downloads.
- You just upload your audio or video file (even up to 5 GB), or paste a link.
- SubtitleBee uses AI and speech recognition to convert spoken words into text, complete with time codes.
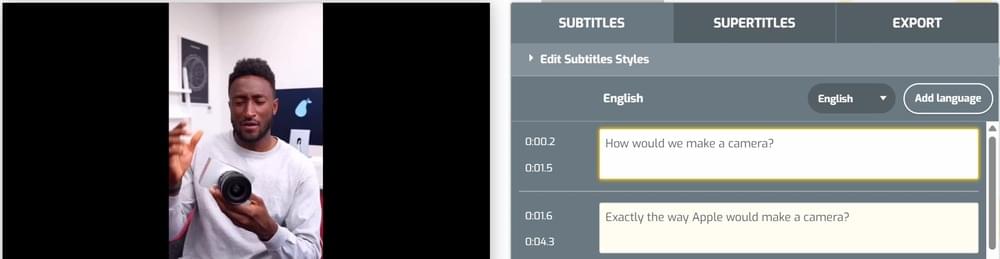
- You can edit the transcript right in the online editor.
- Once satisfied with the editing, click the “Translate Subtitles” option and select the language.
- If you want to translate into more languages click “Add Language”.
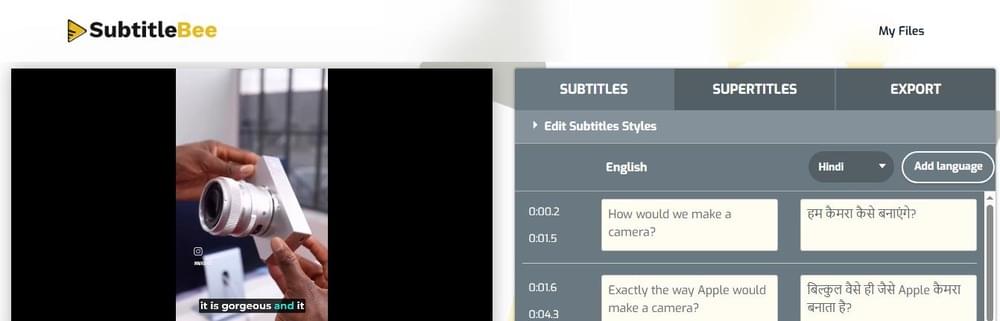
- To export the transcript, go to the EXPORT tab and click the export button. Next, download the transcript in formats like SRT, VTT, TXT, or ASS without using any credits from your paid plan.

That’s all it takes to make your audio or video accessible and searchable for people around the world. Check out some best free transcription services too.
Conclusion
Transcription turns spoken words into written text in the same language. Translation changes that text into another language so more people can understand it.
If you only want written notes, subtitles, or records, transcription is enough. If you want to share your content with people who speak other languages, then you need translation. In many cases, using translation and transcription together give the best results.
You can use an AI subtitle generator to do both. It helps you create accurate transcripts, translate them into over 120 languages, and make your content useful globally.
FAQs
Why should I use transcription and translation together for better results
Transcribing first lets you have an accurate written record, which makes the translation process more precise. SubtitleBee recommends this sequence for the best results.
Which is better for subtitles transcription or translation?
It depends on your audience. If your viewers speak the same language as your content then transcription is enough. Otherwise, you’ll need transcription and translation to create multilingual subtitles.
How do I know if my content needs professional human translation instead of AI tools?
AI tools are fast and cost-effective for general content. Professional human translation is better for sensitive documents like legal contracts, medical texts, or creative writing where accuracy in tone and cultural meaning cannot be avoided.
Is transcription only useful for videos?
No. Transcription can be applied to audio files, meetings, lectures etc. Any spoken material can be transcribed into text.
Does using transcription and translation improve SEO?
Absolutely. Transcripts make your content searchable because search engines can read the text. Adding translations in multiple languages expands your content reach to a wider audience.
Add and translate your subtitles to more than 100 languages with high accuracy